Treatment Method 1
|
|
|
For more information regarding INTERVENT, click here: www.INTERVENT.com/CREST-2
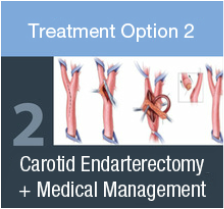
Treatment Method 2
|
|
Carotid Endarterectomy is performed by:
Carotid endarterectomy has been the standard of care for the treatment of carotid stenosis for the last 40 years. |
RISKS
With any surgical procedure, there is a risk of complications. Some of the complications that may arise from carotid endarterectomy include:
|
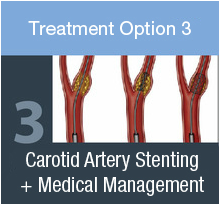
Treatment Method 3
|
|
Carotid Artery Stenting is performed by:
Carotid artery stenting has been a common treatment for carotid stenosis for the more than 20 years. |
RISKS
With any surgical procedure, there is a risk of complications. Some of the complications that may arise from carotid stenting include:
|
Website by The Story Laboratory, LLC